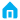
Trimming machine For Precision Bearing seals and shields
Trimmer for Precision Seals;
Angle trimmer for Bearing Seals;



| Product name |
Bearing Seal, Bearing Shield |
| Specification |
#6001 #6002 #6003 #6004 |
| Material |
rubber-metal bonded |
| Main Usage and function |
Sealing, protection |
| Industry & Application |
pumps, motors, gearboxes or conveyors |
| Recommended Machine Model |
YA-MM-200 |
| Production Capacity |
12-15 PCS/min |
VIDEO OF THE TRIMMING PROCESS ON YOUTUBE
You might be interested in learning more about bearing seals and shields—here’s some additional information that could be helpful.
1.The Different Types of Bearing Seals
Whether in pumps, motors, gearboxes or conveyors, bearings depend on effective sealing to perform reliably. Choosing the right bearing seal types means better protection, less downtime and longer equipment life.
2.What Are Bearing Seals?
A bearing seal is a component installed around a bearing or bearing housing to prevent contamination ingress (dust, moisture, debris) and retain lubricant in the bearing chamber. Without proper sealing, even high quality bearings can suffer in performance and life.
Seals help turn standard bearings into “seal bearing” configurations — ready for harsher environments and higher reliability.

3.Why Seal Selection Is Critical
The wrong seal type or material can result in:
Lubricant loss → increased friction & heat
Contaminant ingress → accelerated wear or corrosion
Temperature build‐up → premature failure
Unscheduled maintenance and downtime
Using the correct bearing seal types aligned to your operating environment and loads ensures you get the most from your sealed bearings.
4. Common Bearing Seal Types
Here are the major bearing seal types you’ll find in industrial applications:

These seals make physical contact with a track or ring of the bearing. Because of the contact, they offer high sealing efficiency.
Typical uses: moderate to low speed, abrasive or wet environments.
Pros: strong contaminant exclusion, good lubricant retention.
Cons: slight additional friction, potential heat rise.
In this configuration the seal does not physically touch the bearing race. Rather, there’s a small gap or labyrinth to prevent ingress.
Typical uses: high speed, cleaner environments.
Pros: less friction, better for speed.
Cons: slightly less protection against fine contamination.
A subset of non-contact seals, labyrinth seals use a tortuous path (multiple grooves or chambers) to block contaminants without direct contact.
Typical uses: compressors, large rotating machinery, turbine shafts.
Pros: very reliable under heavy duty use, no frictional contact.
Cons: requires precise design/installation.
- Shielded Bearings (Metal Shields)
Often referred to as “sealed bearings” in general terms, these bearings include integrated shields or covers (e.g., metal plates) to block larger contaminants, while still allowing lubrication to remain.
Typical uses: motors, fans, general industrial equipment.
Pros: low cost, easy to install.
Cons: not as strong as full contact seals in harsh environments.
- Sealed Bearings (Factory Sealed)
These are bearings that arrive pre‐lubricated and already fitted with a seal or shield. They’re ready to install and often maintenance‐free in moderate duty applications.
Typical uses: automotive assemblies, smaller machines, general industrial use.
Pros: minimal maintenance, quick installation.
Cons: limited options for re‐lubrication or extreme environments.
5.Applications & Industry Use-Cases
Below are some typical application scenarios for different bearing seal types:
- Pumps & compressors → often use labyrinth seals or contact seals because of harsh fluid and solid contamination.
- Electric motors and fans → shielded or sealed bearings are common given moderate environments and desire for low maintenance.
- Gearboxes and heavy industrial drives → may require contact seals with backup rings to handle heavy loads and contamination.
- Automotive and small machinery → sealed bearings (pre‐lubed) offer quick installation and minimal service.
Heavy Industrial Equipment
- Mining Equipment - Extreme-duty seals for bearings exposed to abrasive dust, water, and vibration in crushers, conveyors, and screening equipment
- Steel Mill Applications - High-temperature bearing protection for continuous casters, rolling mills, and process equipment operating in harsh thermal environments
- Pulp & Paper Machinery - Specialized seals resistant to process chemicals, steam, and water exposure in roll bearings and rotating equipment
- Heavy Manufacturing - Durable sealing solutions for presses, forming equipment, and machine tools with high mechanical stress
- Power Generation - Long-life seals for critical bearings in turbines, generators, and auxiliary equipment requiring exceptional reliability
- Material Handling Systems - Contamination-resistant designs for conveyor bearings, idlers, and drive systems in dusty environments
- Cement Production - Abrasion-resistant sealing for bearings exposed to cement dust, clinker, and high-temperature conditions
- Woodworking Equipment - Effective protection against fine wood dust, resins, and cutting fluids in high-speed tooling applications
Process Industry Applications
- Chemical Processing - Chemical-resistant bearing protection for pumps, mixers, and agitators handling corrosive media
- Food & Beverage Equipment - FDA-compliant seals for sanitary applications with resistance to frequent washdown and cleaning chemicals
- Pharmaceutical Machinery - Clean, particle-free sealing solutions compatible with GMP requirements and sanitizing procedures
- Oil & Gas Equipment - Specialized seals for bearings in pumps, compressors, and process equipment handling hydrocarbons
- Water Treatment Systems - Durable protection for underwater and chemically exposed bearings in treatment equipment
- Textile Machinery - High-speed shaft seals for spinning, weaving, and finishing equipment with minimal friction
- Plastics Processing - Temperature-resistant seals for extruders, injection molding equipment, and polymer processing
- HVAC Systems - Reliable sealing for fan and blower bearings with optimized lip pressure for energy efficiency
Mobile Equipment Applications
- Construction Equipment - Heavy-duty protection for bearings in articulating joints, wheel hubs, and drive components
- Agricultural Machinery - Specialized seals excluding soil, fertilizers, and crop debris from critical bearings
- Forestry Equipment - Robust sealing solutions protecting bearings from bark, sap, and environmental contamination
- Railway Equipment - Long-life seals for wheel bearings, traction motors, and gearboxes with extended service intervals
- Marine Applications - Corrosion-resistant bearing protection for propulsion systems and deck equipment in saltwater environments
- Material Handling Vehicles - Reliable sealing for lift trucks, loaders, and mobile equipment operating in diverse conditions
- Aviation Ground Support - High-performance seals for equipment operating in airport environments with jet fuel and hydraulic fluid exposure
- Specialized Transport - Custom sealing solutions for unique vehicles and transport systems with specific environmental challenges

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!